LED Control¶
Introduction¶
The LED control (LEDC) peripheral is primarily designed to control the intensity of LEDs, although it can also be used to generate PWM signals for other purposes as well. It has 16 channels which can generate independent waveforms that can be used, for example, to drive RGB LED devices.
A half of LEDC’s channels operate in high speed mode. This mode is implemented in hardware and offers automatic and glitch-free changing of the PWM duty cycle. The other half of channels operate in low speed mode, where the moment of change depends on the application software. Each group of channels is also able to use different clock sources.
The PWM controller can automatically increase or decrease the duty cycle gradually, allowing for fades without any processor interference.
Functionality Overview¶
Getting LEDC to work on a specific channel in either high or low speed mode is done in three steps:
- Configure Timer by specifying the PWM signal’s frequency and duty cycle resolution.
- Configure Channel by associating it with the timer and GPIO to output the PWM signal.
- Change PWM Signal that drives the output in order to change LED’s intensity. This can be done under the full control of software or with hardware fading functions.
As an optional step, it is also possible to set up an interrupt on the fade end.
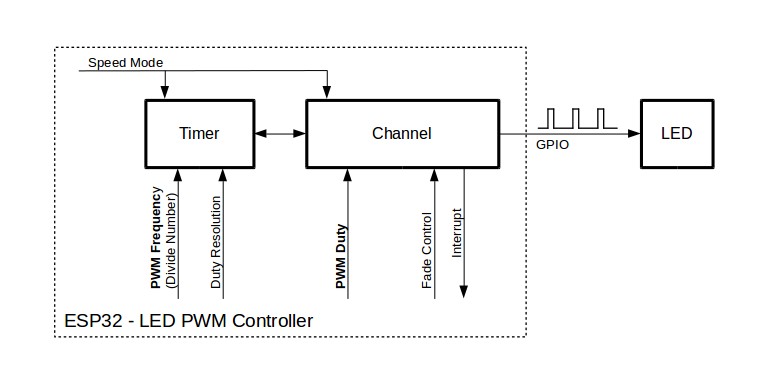
Key Settings of LED PWM Controller’s API
Configure Timer¶
Setting the timer is done by calling the function ledc_timer_config() and passing to it a data structure ledc_timer_config_t that contains the following configuration settings:
- Timer number
ledc_timer_t- Speed mode
ledc_mode_t- PWM signal frequency
- Resolution of PWM duty
The frequency and the duty resolution are interdependent. The higher the PWM frequency, the lower duty resolution is available, and vice versa. This relationship might be important if you are planning to use this API for purposes other than changing the intensity of LEDs. For more details, see Section Supported Range of Frequency and Duty Resolutions.
Configure Channel¶
When the timer is set up, configure a selected channel (one out of ledc_channel_t). This is done by calling the function ledc_channel_config().
Similar to the timer configuration, the channel setup function should be passed a structure ledc_channel_config_t that contains the channel’s configuration parameters.
At this point, the channel should start operating and generating the PWM signal on the selected GPIO, as configured in ledc_channel_config_t, with the frequency specified in the timer settings and the given duty cycle. The channel operation (signal generation) can be suspended at any time by calling the function ledc_stop().
Change PWM Signal¶
Once the channel starts operating and generating the PWM signal with the constant duty cycle and frequency, there are a couple of ways to change this signal. When driving LEDs, primarily the duty cycle is changed to vary the light intensity.
The following two sections describe how to change the duty cycle using software and hardware fading. If required, the signal’s frequency can also be changed; it is covered in Section Change PWM Frequency.
Change PWM Duty Cycle Using Software¶
To set the duty cycle, use the dedicated function ledc_set_duty(). After that, call ledc_update_duty() to activeate the changes. To check the currently set value, use the corresponding _get_ function ledc_get_duty().
Another way to set the duty cycle, as well as some other channel parameters, is by calling ledc_channel_config() covered in Section Configure Channel.
The range of the duty cycle values passed to functions depends on selected duty_resolution and should be from 0 to (2 ** duty_resolution) - 1. For example, if the selected duty resolution is 10, then the duty cycle values can range from 0 to 1023. This provides the resolution of ~0.1%.
Change PWM Duty Cycle using Hardware¶
The LEDC hardware provides the means to gradually transition from one duty cycle value to another. To use this functionality, enable fading with ledc_fade_func_install() and then configure it by calling one of the available fading functions:
Finally start fading with ledc_fade_start().
If not required anymore, fading and an associated interrupt can be disabled with ledc_fade_func_uninstall().
Change PWM Frequency¶
The LEDC API provides several ways to change the PWM frequency “on the fly”:
- Set the frequency by calling
ledc_set_freq(). There is a corresponding functionledc_get_freq()to check the current frequency.- Change the frequency and the duty resolution by calling
ledc_bind_channel_timer()to bind some other timer to the channel.- Change the channel’s timer by calling
ledc_channel_config().
More Control Over PWM¶
There are several lower level timer-specific functions that can be used to change PWM settings:
The first two functions are called “behind the scenes” by ledc_channel_config() to provide a startup of a timer after it is configured.
Use Interrupts¶
When configuring an LEDC channel, one of the parameters selected within ledc_channel_config_t is ledc_intr_type_t which triggers an interrupt on fade completion.
For registration of a handler to address this interrupt, call ledc_isr_register().
LEDC High and Low Speed Mode¶
Of the total 8 timers and 16 channels available in the LED PWM Controller, half of them are dedicated to operation in high speed mode and the other half in low speed mode. Selection of a low or high speed timer or channel is done with the parameter ledc_mode_t that can be found in applicable function calls.
The advantage of high speed mode is glitch-free changeover of the timer settings. This means that if the timer settings are modified, the changes will be applied automatically on the next overflow interrupt of the timer. In contrast, when updating the low-speed timer, the change of settings should be explicitly triggered by software. The LEDC driver handles it in the background, e.g., when ledc_timer_config() or ledc_timer_set() is called.
For additional details regarding speed modes, refer to ESP32 Technical Reference Manual (PDF). Please note that the support for SLOW_CLOCK mentioned in this manual is not yet supported in the LEDC driver.
Supported Range of Frequency and Duty Resolutions¶
The LED PWM Controller is designed primarily to drive LEDs. It provides a wide resolution for PWM duty cycle settings. For instance, the PWM frequency of 5 kHz can have the maximum duty resolution of 13 bits. It means that the duty can be set anywhere from 0 to 100% with a resolution of ~0.012% (2 ** 13 = 8192 discrete levels of the LED intensity).
The LEDC can be used for generating signals at much higher frequencies that are sufficient enough to clock other devices, e.g., a digital camera module. In this case, the maximum available frequency is 40 MHz with duty resolution of 1 bit. This means that the duty cycle is fixed at 50% and cannot be adjusted.
The LEDC API is designed to report an error when trying to set a frequency and a duty resolution that exceed the range of LEDC’s hardware. For example, an attempt to set the frequency to 20 MHz and the duty resolution to 3 bits will result in the following error reported on a serial monitor:
E (196) ledc: requested frequency and duty resolution cannot be achieved, try reducing freq_hz or duty_resolution. div_param=128
In such a situation, either the duty resolution or the frequency must be reduced. For example, setting the duty resolution to 2 will resolve this issue and will make it possible to set the duty cycle at 25% steps, i.e., at 25%, 50% or 75%.
The LEDC driver will also capture and report attempts to configure frequency / duty resolution combinations that are below the supported minimum, e.g.:
E (196) ledc: requested frequency and duty resolution cannot be achieved, try increasing freq_hz or duty_resolution. div_param=128000000
The duty resolution is normally set using ledc_timer_bit_t. This enumeration covers the range from 10 to 15 bits. If a smaller duty resolution is required (from 10 down to 1), enter the equivalent numeric values directly.
Application Example¶
The LEDC change duty cycle and fading control example: peripherals/ledc.
API Reference¶
Header File¶
Functions¶
-
esp_err_t
ledc_channel_config(const ledc_channel_config_t *ledc_conf)¶ LEDC channel configuration Configure LEDC channel with the given channel/output gpio_num/interrupt/source timer/frequency(Hz)/LEDC duty resolution.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
ledc_conf: Pointer of LEDC channel configure struct
-
esp_err_t
ledc_timer_config(const ledc_timer_config_t *timer_conf)¶ LEDC timer configuration Configure LEDC timer with the given source timer/frequency(Hz)/duty_resolution.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_FAIL Can not find a proper pre-divider number base on the given frequency and the current duty_resolution.
- Parameters
timer_conf: Pointer of LEDC timer configure struct
-
esp_err_t
ledc_update_duty(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel)¶ LEDC update channel parameters.
- Note
- Call this function to activate the LEDC updated parameters. After ledc_set_duty, we need to call this function to update the settings.
- Note
- ledc_set_duty, ledc_set_duty_with_hpoint and ledc_update_duty are not thread-safe, do not call these functions to control one LEDC channel in different tasks at the same time. A thread-safe version of API is ledc_set_duty_and_update
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed mode,channel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_stop(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t idle_level)¶ LEDC stop. Disable LEDC output, and set idle level.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_tidle_level: Set output idle level after LEDC stops.
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_freq(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_num, uint32_t freq_hz)¶ LEDC set channel frequency (Hz)
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_FAIL Can not find a proper pre-divider number base on the given frequency and the current duty_resolution.
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_num: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_tfreq_hz: Set the LEDC frequency
-
uint32_t
ledc_get_freq(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_num)¶ LEDC get channel frequency (Hz)
- Return
- 0 error
- Others Current LEDC frequency
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_num: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_duty_with_hpoint(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t duty, uint32_t hpoint)¶ LEDC set duty and hpoint value Only after calling ledc_update_duty will the duty update.
- Note
- ledc_set_duty, ledc_set_duty_with_hpoint and ledc_update_duty are not thread-safe, do not call these functions to control one LEDC channel in different tasks at the same time. A thread-safe version of API is ledc_set_duty_and_update
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_tduty: Set the LEDC duty, the range of duty setting is [0, (2**duty_resolution)]hpoint: Set the LEDC hpoint value(max: 0xfffff)
-
int
ledc_get_hpoint(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel)¶ LEDC get hpoint value, the counter value when the output is set high level.
- Return
- LEDC_ERR_VAL if parameter error
- Others Current hpoint value of LEDC channel
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_duty(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t duty)¶ LEDC set duty This function do not change the hpoint value of this channel. if needed, please call ledc_set_duty_with_hpoint. only after calling ledc_update_duty will the duty update.
- Note
- ledc_set_duty, ledc_set_duty_with_hpoint and ledc_update_duty are not thread-safe, do not call these functions to control one LEDC channel in different tasks at the same time. A thread-safe version of API is ledc_set_duty_and_update.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_tduty: Set the LEDC duty, the range of duty setting is [0, (2**duty_resolution)]
-
uint32_t
ledc_get_duty(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel)¶ LEDC get duty.
- Return
- LEDC_ERR_DUTY if parameter error
- Others Current LEDC duty
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_fade(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t duty, ledc_duty_direction_t fade_direction, uint32_t step_num, uint32_t duty_cycle_num, uint32_t duty_scale)¶ LEDC set gradient Set LEDC gradient, After the function calls the ledc_update_duty function, the function can take effect.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_tduty: Set the start of the gradient duty, the range of duty setting is [0, (2**duty_resolution)]fade_direction: Set the direction of the gradientstep_num: Set the number of the gradientduty_cycle_num: Set how many LEDC tick each time the gradient lastsduty_scale: Set gradient change amplitude
-
esp_err_t
ledc_isr_register(void (*fn)(void *), void *arg, int intr_alloc_flags, ledc_isr_handle_t *handle, )¶ Register LEDC interrupt handler, the handler is an ISR. The handler will be attached to the same CPU core that this function is running on.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Function pointer error.
- Parameters
fn: Interrupt handler function.arg: User-supplied argument passed to the handler function.intr_alloc_flags: Flags used to allocate the interrupt. One or multiple (ORred) ESP_INTR_FLAG_* values. See esp_intr_alloc.h for more info.handle: Pointer to return handle. If non-NULL, a handle for the interrupt will be returned here.
-
esp_err_t
ledc_timer_set(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_sel, uint32_t clock_divider, uint32_t duty_resolution, ledc_clk_src_t clk_src)¶ Configure LEDC settings.
- Return
- (-1) Parameter error
- Other Current LEDC duty
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_sel: Timer index (0-3), there are 4 timers in LEDC moduleclock_divider: Timer clock divide value, the timer clock is divided from the selected clock sourceduty_resolution: Resolution of duty setting in number of bits. The range of duty values is [0, (2**duty_resolution)]clk_src: Select LEDC source clock.
-
esp_err_t
ledc_timer_rst(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_sel)¶ Reset LEDC timer.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_sel: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_timer_pause(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_sel)¶ Pause LEDC timer counter.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_sel: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_timer_resume(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_timer_t timer_sel)¶ Resume LEDC timer.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modetimer_sel: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_bind_channel_timer(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, ledc_timer_t timer_sel)¶ Bind LEDC channel with the selected timer.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel index (0-7), select from ledc_channel_ttimer_sel: LEDC timer index (0-3), select from ledc_timer_t
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_fade_with_step(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t target_duty, uint32_t scale, uint32_t cycle_num)¶ Set LEDC fade function.
- Note
- Call ledc_fade_func_install() once before calling this function. Call ledc_fade_start() after this to start fading.
- Note
- ledc_set_fade_with_step, ledc_set_fade_with_time and ledc_fade_start are not thread-safe, do not call these functions to control one LEDC channel in different tasks at the same time. A thread-safe version of API is ledc_set_fade_step_and_start
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function not installed.
- ESP_FAIL Fade function init error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed mode,channel: LEDC channel index (0-7), select from ledc_channel_ttarget_duty: Target duty of fading [0, (2**duty_resolution) - 1]scale: Controls the increase or decrease step scale.cycle_num: increase or decrease the duty every cycle_num cycles
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_fade_with_time(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t target_duty, int max_fade_time_ms)¶ Set LEDC fade function, with a limited time.
- Note
- Call ledc_fade_func_install() once before calling this function. Call ledc_fade_start() after this to start fading.
- Note
- ledc_set_fade_with_step, ledc_set_fade_with_time and ledc_fade_start are not thread-safe, do not call these functions to control one LEDC channel in different tasks at the same time. A thread-safe version of API is ledc_set_fade_step_and_start
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function not installed.
- ESP_FAIL Fade function init error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed mode,channel: LEDC channel index (0-7), select from ledc_channel_ttarget_duty: Target duty of fading.( 0 - (2 ** duty_resolution - 1)))max_fade_time_ms: The maximum time of the fading ( ms ).
-
esp_err_t
ledc_fade_func_install(int intr_alloc_flags)¶ Install LEDC fade function. This function will occupy interrupt of LEDC module.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function already installed.
- Parameters
intr_alloc_flags: Flags used to allocate the interrupt. One or multiple (ORred) ESP_INTR_FLAG_* values. See esp_intr_alloc.h for more info.
-
void
ledc_fade_func_uninstall(void)¶ Uninstall LEDC fade function.
-
esp_err_t
ledc_fade_start(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, ledc_fade_mode_t fade_mode)¶ Start LEDC fading.
- Note
- Call ledc_fade_func_install() once before calling this function. Call this API right after ledc_set_fade_with_time or ledc_set_fade_with_step before to start fading.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function not installed.
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error.
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel numberfade_mode: Whether to block until fading done.
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_duty_and_update(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t duty, uint32_t hpoint)¶ A thread-safe API to set duty for LEDC channel and return when duty updated.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed modechannel: LEDC channel (0-7), select from ledc_channel_tduty: Set the LEDC duty, the range of duty setting is [0, (2**duty_resolution)]hpoint: Set the LEDC hpoint value(max: 0xfffff)
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_fade_time_and_start(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t target_duty, uint32_t max_fade_time_ms, ledc_fade_mode_t fade_mode)¶ A thread-safe API to set and start LEDC fade function, with a limited time.
- Note
- Call ledc_fade_func_install() once, before calling this function.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function not installed.
- ESP_FAIL Fade function init error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed mode,channel: LEDC channel index (0-7), select from ledc_channel_ttarget_duty: Target duty of fading.( 0 - (2 ** duty_resolution - 1)))max_fade_time_ms: The maximum time of the fading ( ms ).fade_mode: choose blocking or non-blocking mode
-
esp_err_t
ledc_set_fade_step_and_start(ledc_mode_t speed_mode, ledc_channel_t channel, uint32_t target_duty, uint32_t scale, uint32_t cycle_num, ledc_fade_mode_t fade_mode)¶ A thread-safe API to set and start LEDC fade function.
- Note
- Call ledc_fade_func_install() once before calling this function.
- Note
- If a fade operation is running in progress on that channel, the driver would not allow it to be stopped. Other duty operations will have to wait until the fade operation has finished.
- Return
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
- ESP_OK Success
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fade function not installed.
- ESP_FAIL Fade function init error
- Parameters
speed_mode: Select the LEDC speed_mode, high-speed mode and low-speed mode,channel: LEDC channel index (0-7), select from ledc_channel_ttarget_duty: Target duty of fading [0, (2**duty_resolution) - 1]scale: Controls the increase or decrease step scale.cycle_num: increase or decrease the duty every cycle_num cyclesfade_mode: choose blocking or non-blocking mode
Type Definitions¶
-
typedef intr_handle_t
ledc_isr_handle_t¶