Mlink¶
1. Preparation¶
The prerequisite for the ESP-Mesh app to communicate with the ESP-MDF devices is that the device has been successfully networked, and the mobile phone and mesh network are on the same LAN.
The ESP-Mesh app is hereafter referred to as “app” in this document.
The ESP-MDF devices automatically enter the networking stage once configured. If all the networked devices are shown in the ESP-Mesh app, it means that the networking is successful.
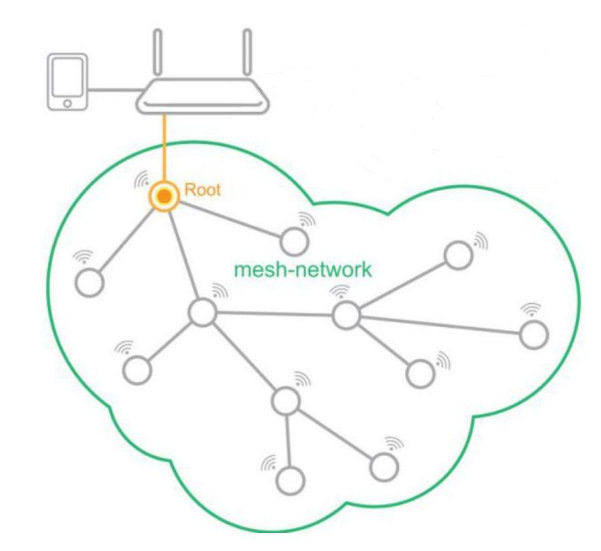
2. Communication Process¶
The root node is the only interface of the mesh network that communicates with external network. To control the devices in the mesh network, the app needs to find the root node; then it obtains the MAC address of all devices in the mesh network from the root node; finally, the root node can communicate with any device on the mesh network. The whole process is divided into three steps:
- The app acquires the IP address, Port number and MAC address of the root node.
- The app inquires a list of the network’s devices from the mesh root node.
- The app and the mesh devices communicate with each other.
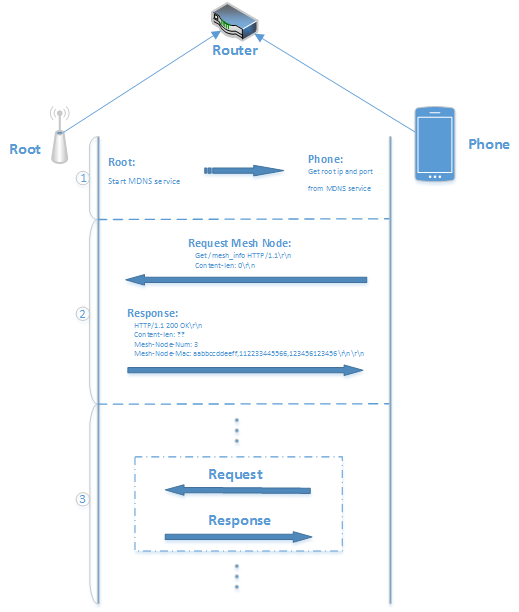
3. Communication Protocol¶
This chapter illustrates the communication protocols involved in the three steps mentioned above. The app gets the list of networked mesh devices, and communicates with devices in the mesh network using the standard HTTP or HTTPS communication protocol. In addition, the communication protocol also includes:
- Device status notification: This is to allow the users to check the real-time status of the device through the app. That is, when the device status changes, the device will send UDP broadcast packets notifying the app of the changes, and then the app will inquire about the updated status of the device.
- Local connectivity control: connectivity control between devices on the LAN.
3.1. App Gets the IP Address, Port Number and MAC Address of the Root Node¶
At this stage, the root node enables the mDNS service and UDP broadcasting function needed for device discovery. During device discovery, the app obtains the IP address, port number, and MAC address of the root node.
- mDNS Service for Device Discovery
The app will then acquire the root node’s IP address through mDNS service, as well as the corresponding port number and MAC address from the port and txt fields of the service info.
mDNS Service Info:
hostname: "esp32_mesh" instance_name: "mesh" service_type: "_mesh-https" proto: "_tcp" port: 80 txt: key: "mac" value: "112233445566"
- Receiving Broadcast UDP Packets
When scanning for devices, the app broadcasts UDP packets and obtains the information about the root node from its reply.
Request:
"Are You Espressif IOT Smart Device?"
Response:
"ESP32 Mesh 112233445566 http 80"
Note
112233445566is the MAC address of the root node80is the http service port- In addition, the app obtains the IP address of the root node through the UDP packets replied by the root node.
3.2. App Acquires the Device List¶
Request::
GET /mesh_info HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.1:80
Response::
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: ??
Mesh-Node-Mac: aabbccddeeff,112233445566,18fe34a1090c
Host: 192.168.1.1:80
Note
/mesh_infois the app command for abtaining the list of devices, which can be implemented via http URL field;Mesh-Node-Macis the list of the node’ Station MAC addresses, separated by commas;Hostis a required field of the HTTP/1.1 protocol, indicating the console’s IP address and port number.
3.3. App and ESP-MDF Device Communication Format¶
- App Requests Format
Request::
POST /device_request HTTP/1.1
Content-Length: ??
Content-Type: application/json
Root-Response::??
Mesh-Node-Mac: aabbccddeeff,112233445566
Host: 192.168.1.1:80
**content_json**
/device_requestis the app command for controlling devices, which, apart from other things, can set and get the device status, via an http request through the URL field.Content-Lengthis the length of the http message body.Content-Typeis the data type of the http message body, in the format ofapplication/json.Root-Responsedecides whether only replies from the root node are needed. If only the replies from the root node are required, the command will not be forwarded to the mesh devices. Value1means replies from the root node are required;0means no reply from the root node is required.
Note
Hostis a required field in the HTTP/1.1 protocol, indicating the app’s IP address and port number.**content_json**is the http message body, corresponding to theRequestin3.4. App's Control of ESP-MDF Devices.
- Device Replies
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: ??
Content-Type: application/json
Mesh-Node-Mac: 30aea4062ca0
Mesh-Parent-Mac: aabbccddeeff
Host: 192.168.1.1:80
\r\n
**content_json**
Content-Lengthis the length of the http message body.Content-Typeis the data type of the http message body, in theapplication/jsonformat.Mesh-Node-Macis the MAC address of the device.Mesh-Parent-Macis the MAC address of the device’s parent node.Hostis a required field in the HTTP/1.1 protocol, indicating the app’s IP address and port.**content_json**is the http message body that corresponding to theRequestin2.4. App's Control of ESP-MDF Devices.
3.4. App’s Control of ESP-MDF Devices¶
- Acquire device information: get_device_info
Request:
{
"request": "get_device_info"
}
requestis field defining the operation on the device, followed by specific commands of operation.
Response:
{
"tid": "1",
"name": "light_064414",
"version": "v0.8.5.1-Jan 17 2018",
"characteristics": [
{
"cid": 0,
"name": "on",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 1,
"min": 0,
"max": 1,
"step": 1
},
{
"cid": 1,
"name": "hue",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 0,
"min": 0,
"max": 360,
"step": 1
},
{
"cid": 2,
"name": "saturation",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 0,
"min": 0,
"max": 100,
"step": 1
},
{
"cid": 3,
"name": "value",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 100,
"min": 0,
"max": 100,
"step": 1
},
{
"cid": 4,
"name": "color_temperature",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 0,
"min": 0,
"max": 100,
"step": 1
},
{
"cid": 5,
"name": "brightness",
"format": "int",
"perms": 7,
"value": 100,
"min": 0,
"max": 100,
"step": 1
}
],
"status_code": 0
}
tidis the type ID of the device, which is used to distinguish different types of devices from each other, such as lights, sockets, and air conditioners.nameis the device name.versionis the device firmware version.characteristicsis the device characteristics, in json format.cidis the characteristic ID of the device,indicating charactertistics such as brightness, hue, switches, etc.nameis the name of the device characteristics.formatis the data format. Four data typesint,double,string,jsonare supported.valueis the value of the device characteristics.minis the minimum value or the minimum length of the data string ofcharacterticsmaxis the maximum value or the maximum length of the data string ofcharacterticsstepis the minimum variation of the characteristics value- When
formatisintordouble,min,``max`` andsteprepresent the minimum value, maximum value, and the minimum variation of the charateristics. - When
formatisstringorjson,minandmaxindicate the minimum and maximum lengths of the string supported respectively, without the keywordstep.
- When
permsstands for permission, parsed in binary integers, with the first bit representing a read permission, the second bit representing a write permission, and the third bit representing a execution permission. Value 0 indicates that the permission is not granted, and value 1 the opposite.- If the parameter has no read permission, the corresponding value can not be accessed.
- If the parameter has no write permission, the corresponding value can not be modified.
- If the parameter has no execution permission, the corresponding value can not be set.
status_codeis the reply to the request commands;0indicates normal, and-1indicates error.
- Acquire device status: get_status
Request:
{
"request": "get_status",
"cids": [
0,
1,
2
]
}
cidsis the field of device characteristics, followed by the CID list of the request.
Response:
{
"characteristics": [
{
"cid": 0,
"value": 0
},
{
"cid": 1,
"value": 0
},
{
"cid": 2,
"value": 100
}
],
"status_code": 0
}
status_codeis the reply to the request command,0indicates normal,-1indicates that the request contains illegal parameters, such as lack of corresponding CID for a device or a value with no read permission in thecidslist.
- Configure the device status: set_status
Request:
{
"request": "set_status",
"characteristics": [
{
"cid": 0,
"value": 0
},
{
"cid": 1,
"value": 0
},
{
"cid": 2,
"value": 100
}
]
}
Response:
{
"status_code": 0
}
status_codeis the reply value to the request command,0indicates normal,-1indicates that the request contains illegal parameters, such as lack of corresponding CID for a device or a value with no read permission in thecidslist.
- Enters the networking mode: config_network
Request:
{
"request": "config_network"
}
Response:
{
"status_code": 0
}
status_codeis the reply value to the request command,0indicates normal,-1indicates error.
- Reboots the device: reboot
Request:
{
"request": "reboot",
"delay": 50
}
``delay`` is the delay for executing the command. This field is not required. The default delay is ``2s``.
Response:
{
"status_code": 0
}
status_codeis the reply to the request command,0indicates normal,-1indicates error.
- Reset the device: reset
Request:
{
"request": "reset",
"delay": 50
}
delayis the delay for executing the command. This field is not required. The default delay is2s.
Response:
{
"status_code": 0
}
status_codeis the reply value to the request command;0indicates normal, and-1indicates error.
3.5. Device Status Notification¶
When the status of the ESP-MDF device (on/off), network connection (connected or disconnected), and route table change, the root node will send broadcast UDP packets to notify the app to obtain the latest status of the device.
UDP Broadcast:
mac=112233445566 flag=1234 type=***
macis the MAC address of the device whose status has changed;flagis a random integer value used to distinguish among notifications at different times;typeis the type of change, including:statusindicates that the device status has changed;httpsindicates that the information of the device connection in the network has changed, and the updated information is required through https communication protocol;httpindicates that the information of the device connection in the network has changed, and the updated information is required through http communication protocol;snifferindicates that a new networked device has been sniffered.